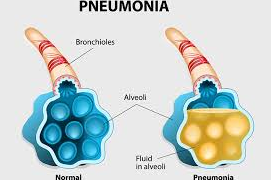
Pneumonia is an infection of the smallest airways of the lungs (alveoli). It can affect children of any age.
Cause
Pneumonia is usually caused by a virus, but can be caused by a germ.
Clinical features
The most striking features of pneumonia in children are a moist cough and a high fever. Sometimes the child is short of breath too and may complain of sharp pains in the chest on breathing deeply. Younger infants may just look very ill and breath rapidly, without having any other symptoms.
Investigations
Pneumonia can usually be diagnosed on clinical grounds, but your doctor may suggest a chest X-ray to confirm the diagnosis. Sputum and blood tests may also be helpful.
Treatment
Some types of pneumonia are due to bacteria which are responsive to antibiotics. It is difficult to distinguish between a viral and a bacterial pneumonia, so sometimes antibiotics are given just to be safe. If the illness is relatively mild, your child can be treated at home with oral medication, bed rest and paracetamol to lower the fever. Use a humidifier in your child’s room to make his breathing easier. Also make sure that your home is smoke-free.
If your child is very ill, admission to hospital may be advised, so that antibiotics can be given intravenously or by injection. Once treatment is commenced, recovery is usually rapid and complete.
When to see your doctor
• if your child has a cough and a high fever;
• if your young baby is listless and breathing rapidly;
• if there is no improvement after 3 days on antibiotics.
Take your child to hospital immediately if his lips look blue.
Cause
Pneumonia is usually caused by a virus, but can be caused by a germ.
Clinical features
The most striking features of pneumonia in children are a moist cough and a high fever. Sometimes the child is short of breath too and may complain of sharp pains in the chest on breathing deeply. Younger infants may just look very ill and breath rapidly, without having any other symptoms.
Investigations
Pneumonia can usually be diagnosed on clinical grounds, but your doctor may suggest a chest X-ray to confirm the diagnosis. Sputum and blood tests may also be helpful.
Treatment
Some types of pneumonia are due to bacteria which are responsive to antibiotics. It is difficult to distinguish between a viral and a bacterial pneumonia, so sometimes antibiotics are given just to be safe. If the illness is relatively mild, your child can be treated at home with oral medication, bed rest and paracetamol to lower the fever. Use a humidifier in your child’s room to make his breathing easier. Also make sure that your home is smoke-free.
If your child is very ill, admission to hospital may be advised, so that antibiotics can be given intravenously or by injection. Once treatment is commenced, recovery is usually rapid and complete.
When to see your doctor
• if your child has a cough and a high fever;
• if your young baby is listless and breathing rapidly;
• if there is no improvement after 3 days on antibiotics.
Take your child to hospital immediately if his lips look blue.
No comments:
Post a Comment